BREAST AUGMENTATION
 Breast implants Breast implants
Breast augmentation surgery involves using breast implants to increase the volume of the breast.
Currently used prostheses are made of silicone, a material in use for 40 years so far and widely studied.
In particular, numerous scientific studies carried out on the subject have excluded any possible correlation between silicone implants and breast cancer, connective tissue diseases, fetal abnormalities or genetic alterations.
If compared to the past, the implants currently used contain a more cohesive silicone gel, and have a thicker wall.
These characteristics make them more resistant and eliminate the risk of migration of Silicon in the very rare cases of rupture of the implant.
Examination
The new cup-size is agreed with the patient.
Supposedly , there are no limits to the breast volume that can be reached; in practice, however, because the result must be as natural as possible, it is more appropriate to achieve a breast size proportionate to the physical characteristics of the patient: a massive breast in a patient who is slim and rather short is likely to be immediately recognized as "fake boobs". If on the contrary, the breast is small and drained (e.g. as a result of a pregnancy) the surgeon will suggest to associate it to a mastopexy.
Surgical procedure
The surgical procedure is performed in general anesthesia and lasts about an hour. The surgical access routes most commonly used are the submammary, the periareolar and the axillary.
I do prefer to use the submammary path which involves a scar the length of about four cm, normally concealed within itself, and that may be visible only in case of bad scarring course when the patient raises their arms. This access allows an accurate positioning of the graft, and does not alter in any way the mammary gland. The implant is usually placed between the mammary gland and the pectoral muscle, without thereby affecting the ability of lactation or the subsequent execution of exams such as ultrasound or mammogram. In some cases, when the patient is very lean and has a very thin chest skin, the implant is placed below the pectoral muscle. This increases the thickness of the tissues that cover the implant, while softening the outline thus giving a more natural result.
After-surgery
Already on the day after the surgery, the patient will be discharged from hospital, wearing a slightly elastic bra, which she will be wearing for a week during which time she will have to avoid any kind of efforts . Sutures are normally completely internal and do not generally require removal.
After fifteen to twenty days, the patient can resume any kind of sporting activity. In later years, may may actually breastfeed and submit to exams normally required for routine prevention of breast cancer, reporting to the radiologist the presence of implants.
How long do breast implants last?
No material implanted in the body lasts forever. For example, even heart implant or hip prosthesis, which require far more invasive surgical approaches, need to be replaced over the time.
Although scientific studies on breast implants showed no harmful effects on the body, on the other hand, they have demonstrated that they become more "fragile" over the time.
This aspect, though, mainly involved implants used in the past, whose walls were much less resistant than the ones currently used. It is therefore likely that the implants currently used last longer.
However, it is proper to inform the patient that 10 to 15 years after surgery, it may be advisable to undergo breast ultrasound check (i.e. without the use of radiation) to assess the integrity of the implants. In any case, even a possible detection of rupture should not scare, as it involves no real risks to health, since silicone remains inside the capsule that normally forms around the implant itself. In case a breakage of the implant is diagnosed sonographically, it is advisable for the patient to have the implants replaced.
Possible complications and side effects
The possible complications involving breast augmentation are those typically arising from any surgical intervention, such as the appearance of a hematoma or infection.
To prevent them, some measures are adopted, such as not taking any anti-inflammatory drugs over the week before the operation so as to avoid an increased risk of bleeding, and the prescription of antibiotics after surgery.
A possible peculiar complication of breast implants is represented by the appearance of "capsular contractions. Human body always forms a soft-consistency capsule around the implant usually not visible nor perceptible to the touch.
In some cases, this capsule is thicker than normal and compresses the implant, which may take on a spherical appearance.
Contraction is usually an aesthetic problem, although in some cases it may cause pain.
Unfortunately, this complication is not predictable, as it depends on each individual's response to specific foreign material. Its treatment involves the use of drugs that have proved to be useful in reducing the fibrotic reaction or, in some case, the replacement of the implants. Equally unpredictable is the quality of the scar in the submammary furrows: despite sutures are made so as to minimize any possible sign, in some patients scarring is not optimum quality and may remain visible at a distance of time.
| BEFORE AND AFTER |
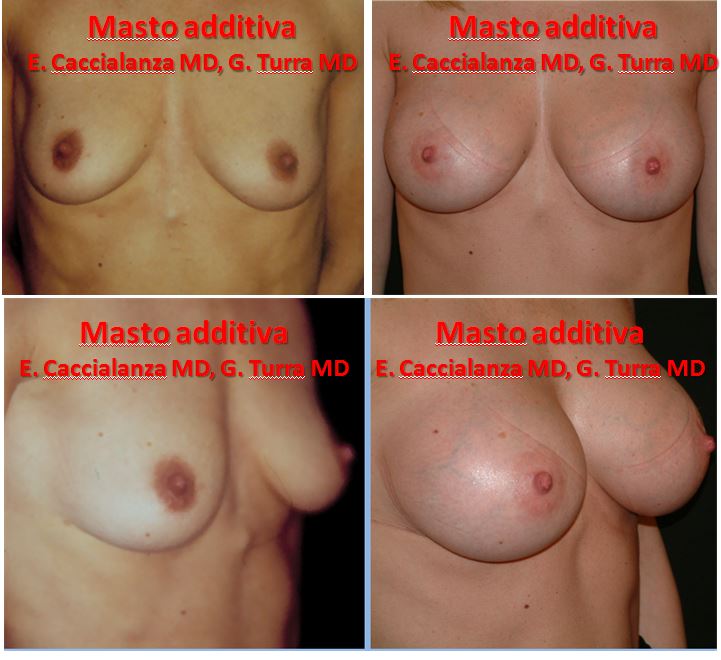
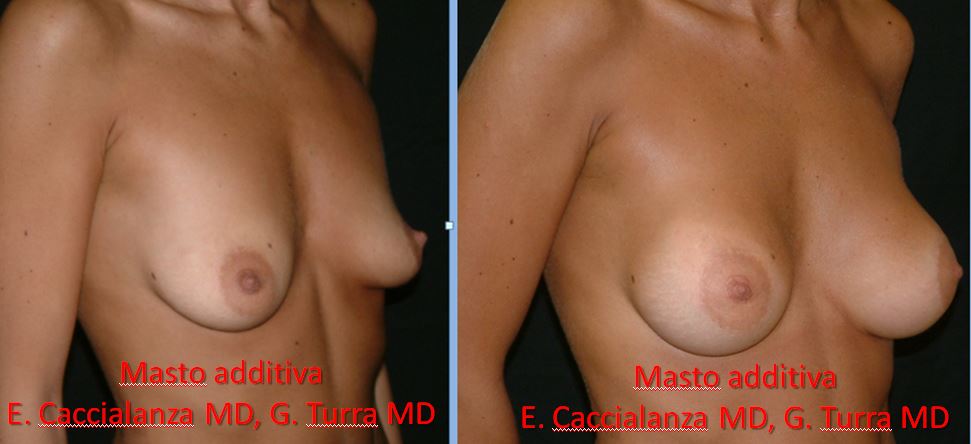
|
|



















